PrEP: What It Is and How Sex Workers Can Use It
Lindsay Roth cowrote this post with sex worker ally and colleague Cassie Warren. Roth and Warren work together at PxROAR (Research, Outreach, Advocacy, and Representation), a program for community activists which offers training and support around biomedical HIV prevention research and advocacy. Readers can contact them with questions about PrEP at lindsay@swopusa.org and cassandra.r.warren@gmail.com.
So you’re telling me you can take a pill to prevent HIV?
Yup. We believe that if done right, PrEP has the potential to be one of the best tools brought to market for receptive partner protection and power since the pill in the 1960’s. PrEP doesn’t double as a contraceptive, but it does reduce your risk of HIV by 90% when taken correctly. It’s still a sweet tool to have in your make-up bag, hard femme box, tool kit, whatever you call it. We are still in the middle of an epidemic, with trans and cis women, men who have sex with men, and injection drug users still being hit hard and unjustly. We deserve to have access to all the options that protect us against HIV.
In what follows, we’d like to lay out the basics of PrEP (no really, what is it? does it cost the first month’s rent?), add context to some of the controversies, and offer our take on what this means for sex workers. We do not anticipate that we’ll be able to answer all the questions people have in this one post, and we hope that you will comment or reach out to us directly if you’d like to know more.
What the heck is it?
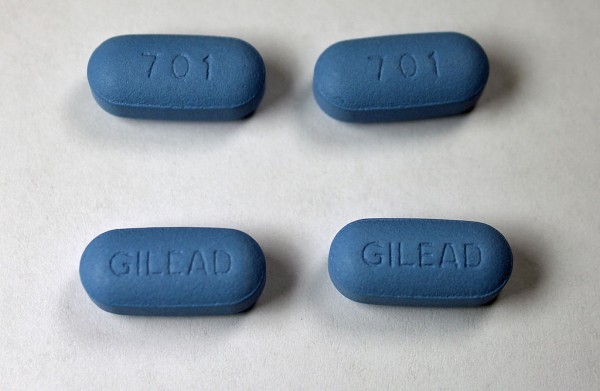
PrEP stands for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis. The main part to note here is “pre,” implying treatment before exposure. In this context, we are talking about exposure to HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). So, PrEP is a medication an HIV-negative person would take to prevent them from becoming positive. Currently, Truvada is the only form of PrEP approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
Truvada is an NRTI (nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor) which is just a fancy name for an HIV medication. It has been used to treat HIV since 2004. We used to know HIV as the virus that caused AIDS, and knew AIDS as a death sentence. However, because of advancements in the treatment of HIV, positive folks can live long, healthy lives. Folks can even be positive, on treatment, and unable to transmit the virus to anyone else. Recently the medical establishment stopped giving AIDS diagnoses: Because of new treatment options people can be at various stages in their HIV diagnosis, and we now classify HIV as stage 0, 1, 2 or 3 HIV.
Many readers may be familiar with PrEP’s sibling, PEP, or post-exposure prophylaxis, the use of antiretroviral drugs—ARVs (again, a fancy name for HIV medications)—to mitigate the risk of HIV transmission after a potential exposure. Any doctor can write a prescription for PEP, most Medicaid programs pay for it, and Gilead, the large research based pharmaceutical company which makes Truvada, has a patient assistance program to cover the the costs for the uninsured or underinsured, regardless of immigration status.
To summarize, PrEP vs. PEP:
- Truvada as PrEP is taken before an exposure to HIV, specifically one pill a day, every day.
- PEP is taken after an exposure to HIV, specifically within 72 hours, and consists of 30 days of full-regimen HIV treatment medication.
- Both prevent you from acquiring HIV.
How does PrEP work?
The rationale behind PrEP is based on the way most doctors are treating HIV-positive individuals with ARVs. Truvada is a combination of two medications, tenofovir and emtricitabine. If HIV is presenting itself in one’s body, this medication blocks the replication of HIV in the body. Doctors currently prescribe one pill a day, as the medication must be present in the body to do its work. However, there are trials underway to test the efficacy of other ways of taking PrEP. So far, the results of the iPrEX OLE (open label extension) say that if you take it 2-4 times a week you are protected 85% of the time against HIV, and if you take it 5-7 times a week, you are protected 99% of the time against HIV (not other STIs or pregnancy). If you take it less than 2 times a week you have zero protection. 1
Can I take it right before I meet a date?
No. PrEP acts like a full metal jacket around your T-cells, so if HIV is introduced to your body it can’t get into the cells it wants to infect and replicate itself.2 It takes about seven days to make this metaphorical metal jacket around the cells in the rectum (drugs taken orally are absorbed quicker in the digestive track), and about 20 days to make a metal jacket around the cells in the vagina (our apologies if you call your junk something else) and in the bloodstream. So, for full protection, you’d need to be taking it every day for a week before you’re protected during anal sex, and every day for three weeks before you are protected during vaginal sex or during any activity in which you would share blood (e.g., sharing needles for tattoos, hormones, drugs, piercings, etc.).



 Danielle is the Care Coordinator for
Danielle is the Care Coordinator for